
It took over nine days in April 2012 and thirteen days in October 2012, during 312 orbits at 824 kilometers (512 miles) to capture the whole Earth.
The main image of the Earth at night (2012) was captured by NASA using the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership (Suomi NPP) satellite. Two versions of the images are available: Deserts in Africa, Arabia, Australia, Mongolia, and the United States are poorly lit as well (except along the coast and rivers), along with the boreal forests of Canada and Russia, and the great mountains of the Himalaya. The interior jungles of Africa and South America are mostly dark. Some regions remain thinly populated and unlit. The Nile River, from the Aswan Dam to the Mediterranean Sea, is another bright thread through an otherwise dark region. In Russia, the Trans-Siberian railroad is a thin line stretching from Moscow through the center of Asia to Vladivostok. The United States interstate highway system appears as a lattice connecting the brighter dots of city centers. Cities tend to grow along coastlines and transportation networks. The brightest areas of the Earth are the most urbanized, but not necessarily the most populated (compare western Europe with China and India). The freeform surfaces are validated for several numerical examples using a ray-tracer based on Quasi-Monte Carlo simulation.The Night Earth map shows the lights that are visible at night on the Earth's surface. The algorithm is capable to compute two solutions of the Monge–Ampère boundary value problem, corresponding to either c-convex or c-concave freeform surfaces for both layouts. Numerical solutions are computed using a generalized least-squares algorithm which is presented by Yadav et al. 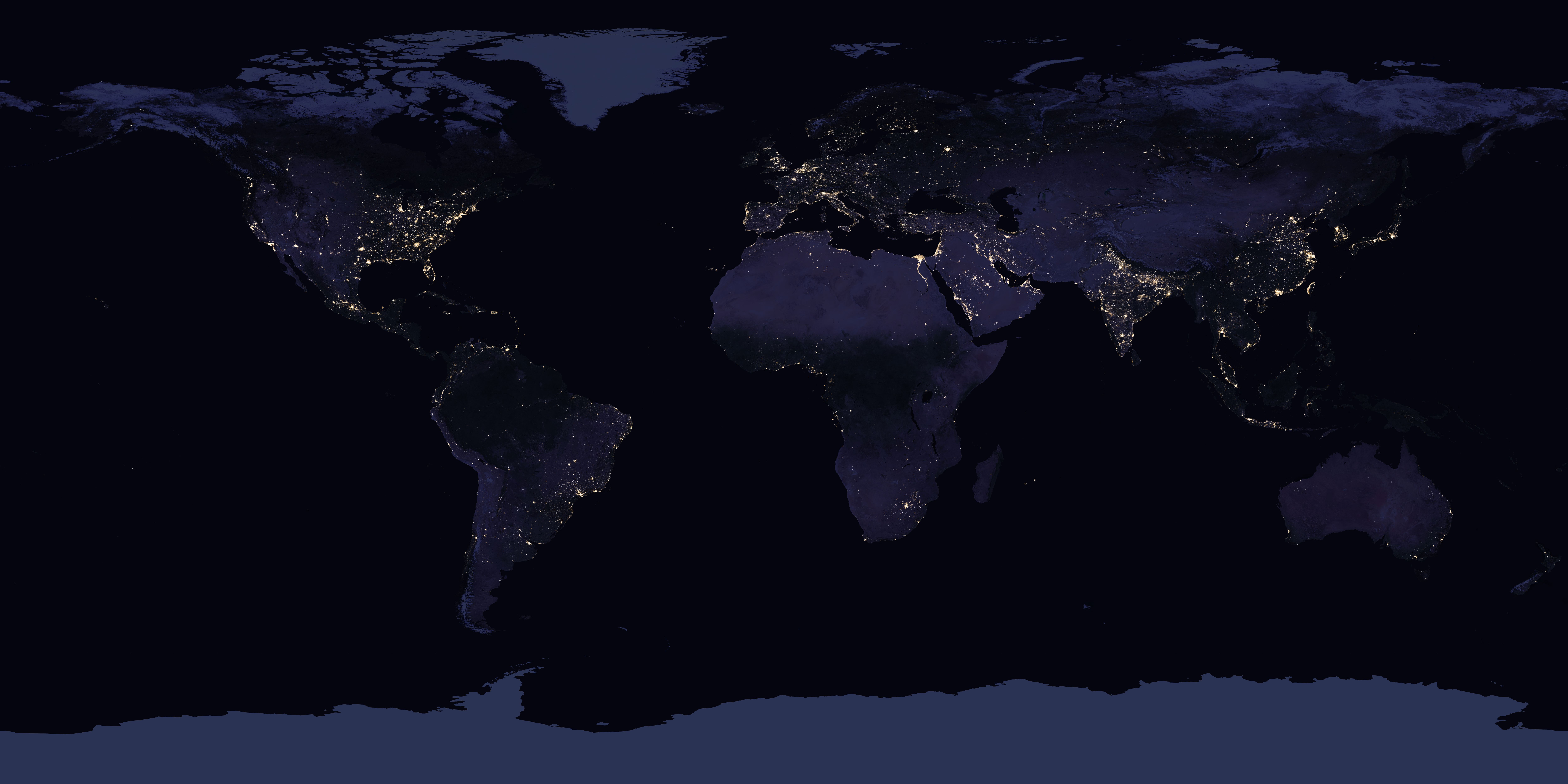
The freeform lens design problem can be formulated as a Monge–Ampère type differential equation with transport boundary condition, expressing conservation of energy combined with the law of refraction and the constraint imposed on the optical path length between source and target planes.

Two different layouts of the freeform lens optical system are introduced, i.e., a single lens with double freeform surfaces, and two separate lenses with two flat and two freeform surfaces. Double freefrom surfaces are utilized to shape collimated beams. In this article, we present a formulation for the design of double freeform lens surfaces to control the intensity distribution of a laser beam with plane wavefronts.






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
